5 Common Root Cause Analysis Tools for More Effective Problem-Solving

Prefer to listen to this post instead? Here’s the audio version:
Next to accurately defining a problem, root cause analysis (RCA) is one of the most important elements of problem-solving in quality management. Effective RCA ensures that the actual cause of a problem is identified and addressed, preventing recurrence.
This is where methodologies like Six Sigma, with its DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework, come into play. Six Sigma provides a structured approach that complements RCA tools. It ensures a thorough analysis and sustainable improvement in quality processes.
As you can see, defining the problem is the first step. It’s crucial to identify the right tool for determining the real cause of a problem and prioritizing its solution.
Should you use fault tree analysis, which uses boolean logic, or FMEA, which combines qualitative and quantitative methods? Which is the best root cause analysis tool type for you?
No matter which approach you choose, it’s equally important that your RCA tasks and results are digitized, and not on paper or in an Excel spreadsheet. By going digital, you’ll have more structure, visibility and data in every investigation.
What’s even more powerful is integrating root cause analysis with your audit management system. Not only will you have your entire problem-solving history in one place, but you can also guide your teams, capture information and analyze trends more effectively.
Manufacturers have a range of methods, tools and techniques at their fingertips, each of which is appropriate for different situations. Below, we discuss five common root cause analysis tools:
- Pareto Chart
- The 5 Whys
- Fishbone Diagram
- Scatter Diagram
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Download our free Root Cause Analysis 101 Guidebook
Read 14 quality metrics every executive should know
1. Pareto Chart
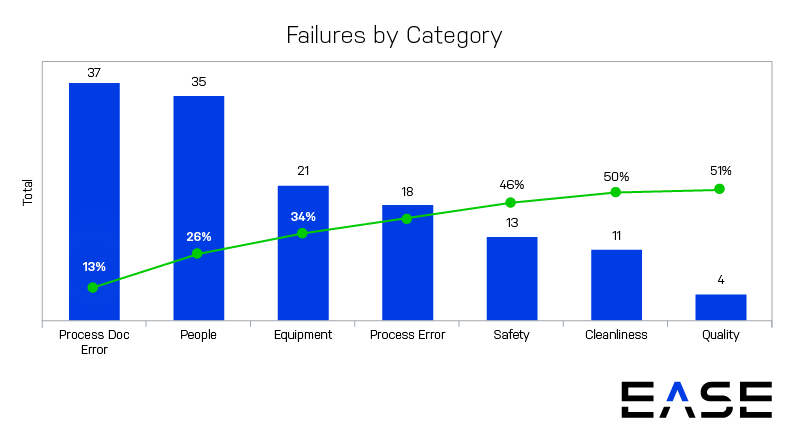
A Pareto chart is a histogram or bar chart combined with a line graph that groups the frequency or cost of different problems to show their relative significance. The bars show frequency in descending order, while the line shows cumulative percentage or total as you move from left to right.
The example above is a report from layered process audit software that groups together the top seven categories of failed audit questions for a given facility. Layered process audits (LPAs) allow you to check high-risk processes daily to verify conformance to standards. LPAs identify process variations that cause defects, making Pareto charts a powerful reporting tool for analyzing LPA findings.
These charts are one of the seven basic tools of quality described by quality pioneer Joseph Juran and are based on Pareto’s law, also called the 80/20 rule. This rule says that 20% of inputs drive 80% of results.
Learn how to create Pareto charts in this post or download the Pareto Chart Tip Sheet and Sample Excel File
2. 5 Whys
The 5 Whys is a method that uses a series of questions to drill down into successive layers of a problem. The basic idea is that each time you ask why, the answer becomes the basis of the next why. It’s a simple tool useful for problems where you don’t need advanced statistics, so you don’t necessarily want to use it for complex problems.
One application of this technique is to more deeply analyze the results of a Pareto analysis. Here’s an example of how to use the 5 Whys:
Problem: Final assembly time exceeds the target
- Why is downtime in the final assembly higher than our goal? According to the Pareto chart, the biggest factor is operators needing to constantly adjust Machine A
- Why do operators need to constantly adjust Machine A? Because it keeps having alignment problems
- Why does Machine A keep having alignment problems? Because the seals are worn
- Why are Machine A’s seals worn? Because they aren’t being replaced as part of our preventive maintenance program
- Why aren’t they being replaced as part of our preventive maintenance program? Because seal replacement wasn’t captured in the needs assessment
Of course, it may take asking why more than five times to solve the issue—the point is to peel away surface-level issues to find the root cause of the problem.
Learn more about the 5 Whys method in this blog post or download our free 5 Whys worksheet.
3. Ishikawa Fishbone Diagram
One way to analyze a problem is to draw it out. Being able to see the information organized visually can make it easier to determine the cause and effect of the problem.
A fishbone diagram sorts possible causes into categories that branch off from the original problem. Also called a cause-and-effect or Ishikawa diagram, this tool may have multiple sub-causes branching off each identified category.
The main problem or effect is placed at the “head” of the fish, and the various causes are drawn as “bones” branching off from the main line. These branches are typically grouped into major categories such as People, Methods, Machines, Materials, Measurements, and Environment, though these categories can be customized depending on the specific context.
Each major category can have smaller branches that delve deeper into more specific sub-causes, helping to organize and prioritize potential causes of the problem systematically.
Learn more about how to use a fishbone diagram in this blog post and download our free set of fishbone diagram templates
4. Scatter Plot Diagram
A scatter plot or scatter diagram uses pairs of data points to help uncover relationships between variables. A scatter plot is a quantitative method for determining whether two variables are correlated, such as testing potential causes identified in your fishbone diagram.
Making a scatter diagram is as simple as plotting your independent variable (or suspected cause) on the x-axis, and your dependent variable (the effect) on the y-axis. If the pattern shows a clear line or curve, you know the variables are correlated and you can proceed to regression or correlation analysis.
Download a free tip sheet to start creating your own scatter diagrams today!
5. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a method used during product or process design to explore potential defects or failures. An FMEA chart outlines:
- Potential failures, consequences and causes
- Current controls to prevent each type of failure
- Severity (S), occurrence (O) and detection (D) ratings that allow you to calculate a risk priority number (RPN) for determining further action
When applied to process analysis, this method is called process failure mode and effects analysis (PFMEA). Many manufacturers use PFMEA findings to inform questions for process audits, using this problem-solving tool to reduce risk at the source.
No matter which tool you use, root cause analysis is just the beginning of the problem-solving process. Once you know the cause, the next step is implementing a solution and conducting regular checks to ensure you’re holding the gain and achieving sustainable continuous improvement. By using software to digitize and manage all this in one place, you’ll simplify collaboration, improve accountability and give your customers confidence in your processes.